Whenever you purchase a automobile, there may be the sticker value and what you really paid after haggling with the vendor over reductions. For prescribed drugs, the media sometimes studies on listing costs that are analogous to the “sticker value” for automobiles. Nevertheless, what actually issues is the web value, which is the value after reductions and rebates. One key query is, how nicely do Medicare Half D plans do at negotiating costs down from their listing value.
A paper by Ippolito and Levy (2023) goals to reply that query utilizing 2007-2019 information on drug costs and rebates from SSR Well being and information on drug utilization from Medical Expenditure Panel Survey (MEPS).
Utilizing these information, they evaluate the relative measurement of rebates for branded drug primarily based on she share of sufferers who use the drug which can be lined by Medicare Half D. The authors discover that:
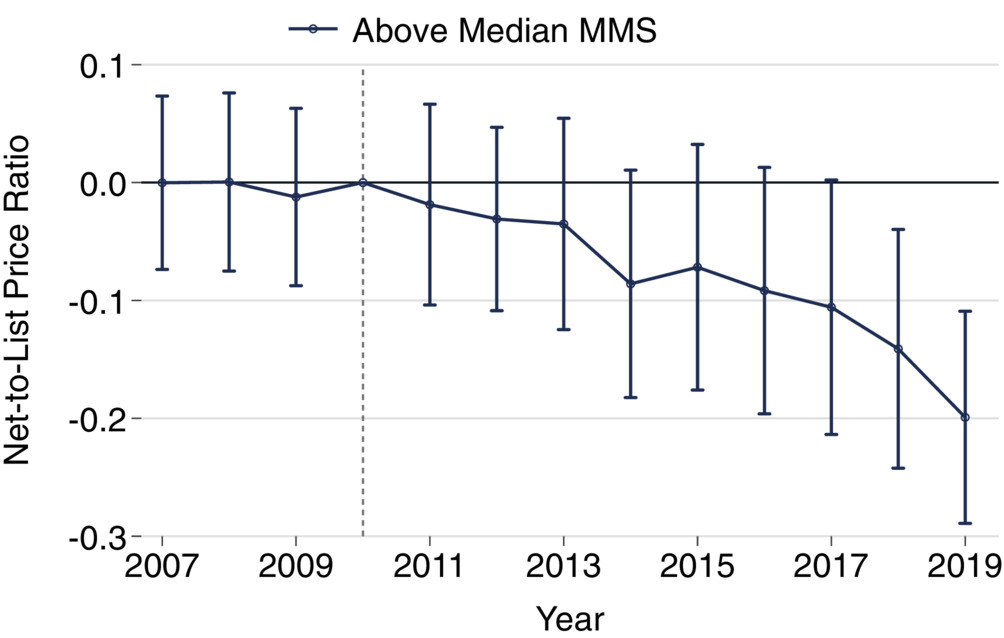
Web-to-list value ratios have been negatively correlated with [Medicare market shares] MMS within the later years of our pattern. In 2019, a ten% improve in MMS was related to a big 4.6% [95% CI: 2.1%, 7.1%] lower in net-to-list ratio. Distinction-in-differences confirmed net-to-list value ratios of medicine with above median MMS fell relative to these with beneath median MMS. By 2019, we observe an absolute discount of −0.2 [95% CI: −0.29, −0.11], representing 28% discount relative to the common ratio in 2010.
The examine excludes doctor administered medication and medicines which can be sometimes prescribed (i.e., <200,000 prescriptions).
The examine finds that this relationship is stronger in later years, and hypothesize that modifications in Half D profit design type the Inexpensive Care Act and Bipartisan Finances Act of 2018 have been a big motive for these further reductions. The authors describe the particular coverage change as follows:
In 2011, the Inexpensive Care Act phased the protection hole down by requiring that producers provide a 50 p.c low cost off of listing value on model medication in that portion of the profit. Along with decreasing spending by enrollees, these reductions have been handled as if the enrollee had really spent that cash for functions of figuring out the place the beneficiary was within the profit design. The Bipartisan Finances Act of 2018 elevated these reductions to 70 p.c, which lowered plan legal responsibility on this section to simply 5 p.c.
Is that this a great factor? In a partial equilibrium sense, the reply is ‘sure’. Decrease web costs are good for Medicare’s backside line. Nevertheless, rising the rebates and reductions that producers possible will outcome both in increased listing costs–in order that the web value stays fixed–or the quantity of R&D investments and new medication coming to market will fall as drug reimbursement turns into much less beneficiant. Like something in well being economics, there are all the time tradeoffs.